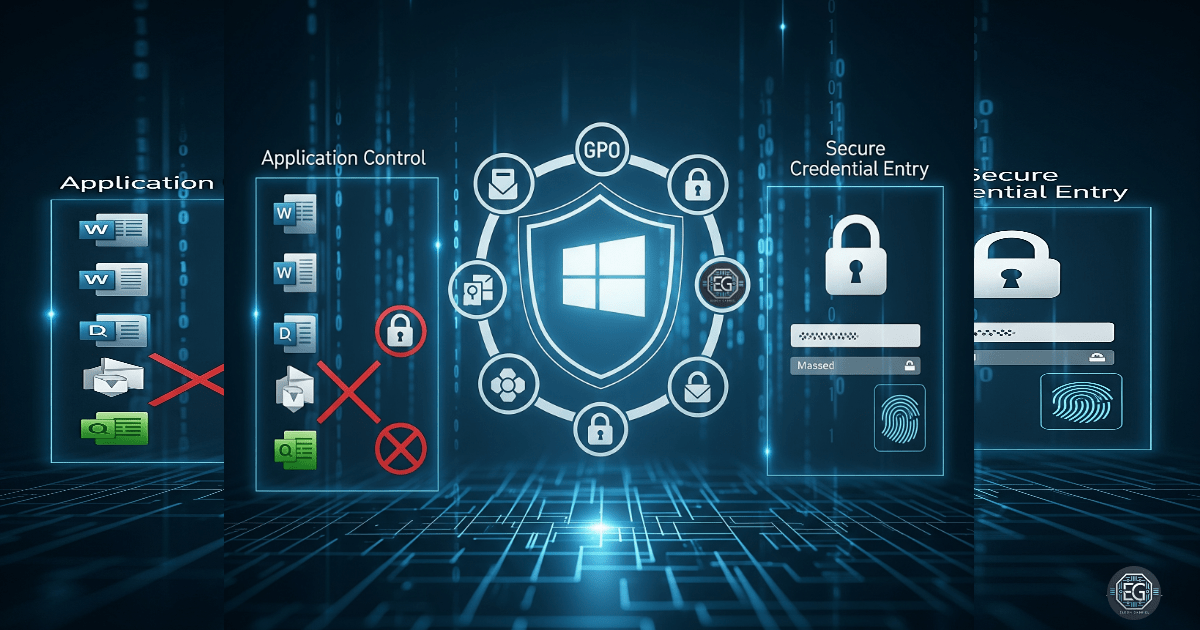
This blog covers two practical exercises I completed in Windows system hardening using Group Policy Objects (GPOs). First, I restricted the ability to install applications to reduce risk from unauthorized software. Second, I enforced secure credential entry to protect sensitive logins from malware or local attacks.
Exercise Core Function
- Restrict application installations via GPO to prevent unauthorized software.
- Enforce secure credential entry with Secure Desktop and logon restrictions.
What I Studied
- Explored Local Group Policy settings for application installation control and credential management.
- Configured Secure Desktop and credential entry restrictions for safer logons.
- Used tools and commands like
gpedit.mscandgpresult /rto verify policy enforcement. - Practiced understanding Windows security options, including credential UI, logon behavior, and administrative account enumeration.
- Applied these configurations in line with endpoint security best practices and system hardening frameworks.
What I Learned
- GPOs are a powerful way to enforce security policies at the endpoint level.
- Hands-on lab experience highlighted the importance of testing policies before enterprise deployment.
- Observed that small changes, like disabling automatic logon or restricting software installs, significantly reduce attack surfaces.
- Learned troubleshooting steps for policy enforcement, including verifying effective settings and understanding policy precedence.
Why It Matters
- Properly configured GPOs help prevent unauthorized software installation and credential theft, reducing enterprise risk.
- These exercises demonstrate real-world ways to enforce compliance, strengthen endpoint security, and reduce lateral movement by attackers.
- Even small configuration changes can have a significant impact on operational security and protecting sensitive data.
How It Maps to the Job / Framework
- These exercises map to System Administrator / Security Operations roles (NIST NICE: Protection and Defense Awareness and Training (PR.AT), Information Protection Processes and Procedures (PR.IP)), focusing on access control and endpoint protection.
- Skills gained are directly applicable in professional environments for hardening Windows endpoints, mitigating insider threats, and supporting compliance frameworks like ISO 27001 or NIST CSF.
Key Takeaways
- GPOs enable administrators to enforce critical security policies across endpoints.
- Testing policy application is essential before enterprise-wide rollout.
- Small configuration changes, like secure logon enforcement and application restriction, greatly reduce risk.
- Hands-on labs bridge theory with real-world cybersecurity application.