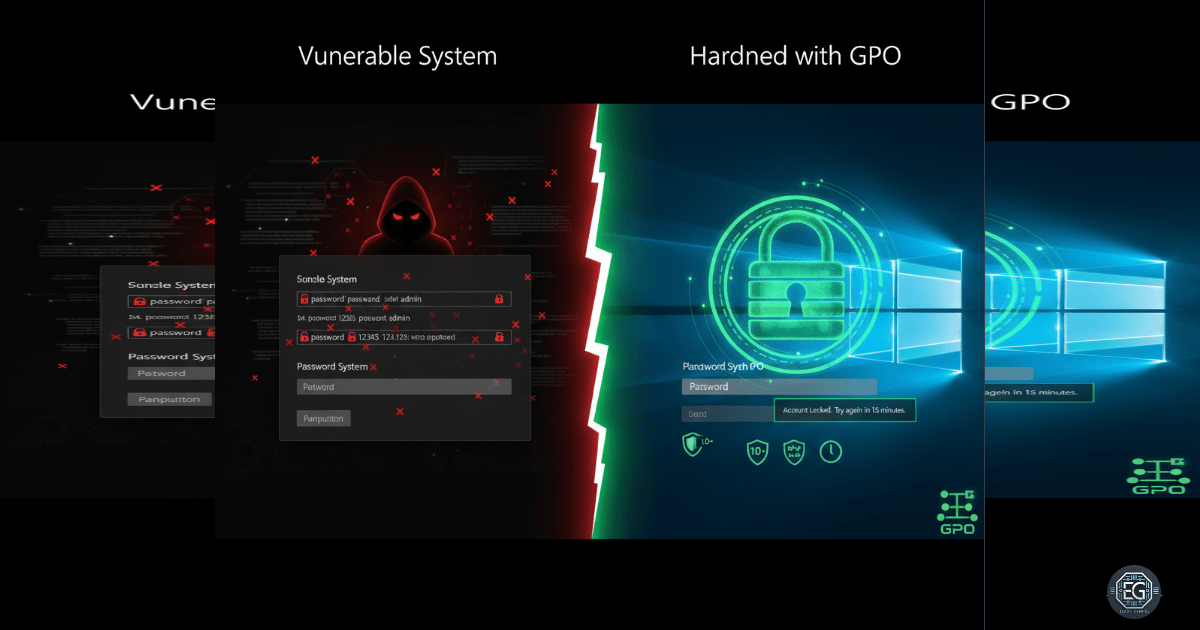
Strengthening authentication controls is one of the most effective ways to stop attackers before they ever get inside a system. In this exercise, I configured a Windows 10 machine with strict password and account lockout settings using the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc). The goal: defend against password guessing and brute-force attacks by eliminating weak sign-in options and enforcing strong password rules.
Applying the Policy
I used Local Group Policy paths to configure three main areas:
Logon Policy
Disabled convenience PIN sign-in to remove weaker authentication fallbacks.
Password Policy
- Minimum password length: 10 characters
- Password complexity: Enabled (uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols)
- Password history: 5 remembered passwords
- Maximum password age: 90 days
- Minimum password age: 24 hours
- Reversible encryption: Disabled
Account Lockout Policy
- Threshold: 5 failed logon attempts
- Lockout duration: 15 minutes
- Reset counter after: 15 minutes
Verification steps included forcing policy updates with gpupdate /force, reviewing settings in secpol.msc, and simulating failed login attempts to confirm lockout behavior.
Why This Matters
Weak or reused passwords remain one of the top entry points for attackers. By enforcing length, complexity, and lockout controls, organizations dramatically reduce the success rate of brute-force attempts.
Even in a single-machine lab, these principles scale directly to enterprise environments via Active Directory GPOs. This approach supports compliance with CIS Benchmarks, NIST 800-53, and similar industry standards.
For non-technical readers: imagine a door that automatically bolts itself after someone tries the wrong key too many times. That’s what account lockout policies do for user accounts.
Professional Relevance
This exercise reinforces skills aligned to:
- NICE Framework – System Administration (OM-SA-001): Configuring operating system security settings and enforcing organizational policies.
- ASD Cyber Skills Framework – System Hardening: Applying technical controls that reduce vulnerabilities and enforce compliance with security standards.
These tasks directly map to the work of IT Operations Technicians and junior Security Administrators responsible for day-to-day system defense.
Key Takeaways
- Password complexity and expiration strengthen authentication baselines.
- Account lockout policies disrupt brute-force and password guessing attacks.
- Verification matters — security settings only count if they are tested.
- Lab-based configurations scale directly into enterprise compliance baselines.
For the full step-by-step process and deeper insights, see my full report below: